Subdomain vs Subdirectory: What's the Difference and Which One Is Better for SEO?

I have seen websites with addresses like blog.domain.com and asked myself how that’s different from something like domain.com/blog?
These two url — Subdomains & Subdirectories, might seem similar , but they can have a big effect on your SEO strategy, site structure and user experience.
In This Article You’re going to get familiar about:
- What subdomains and subdirectories are
- Key differences between them
- Which one is better for SEO
- Real examples
- How to create them with Spaceship — a powerful and affordable domain provider
What Is a Subdomain?
A subdomain is a prefix added before your main domain to separate a section of your site.
Example:
- blog.domain.com
- app.domain.com
This is especially helpful if you want to isolate certain services like:
- A blog
- An e-commerce store
- A web app
- Language versions of your site (en.domain.com)
What Is a Subdirectory?
A subdirectory is a folder that lives under your main domain.
Example:
- domain.com/blog
- domain.com/about
Subdirectories are part of the same website and share the domain authority of the base site. Google typically considers them as one website, unlike subdomains.
You can also track traffic to your web app using Plausible Analytics — a fast, cookie-free alternative to Google Analytics. I documented the setup in my Plausible tutorial.
Subdomain vs Subdirectory: SEO Comparison
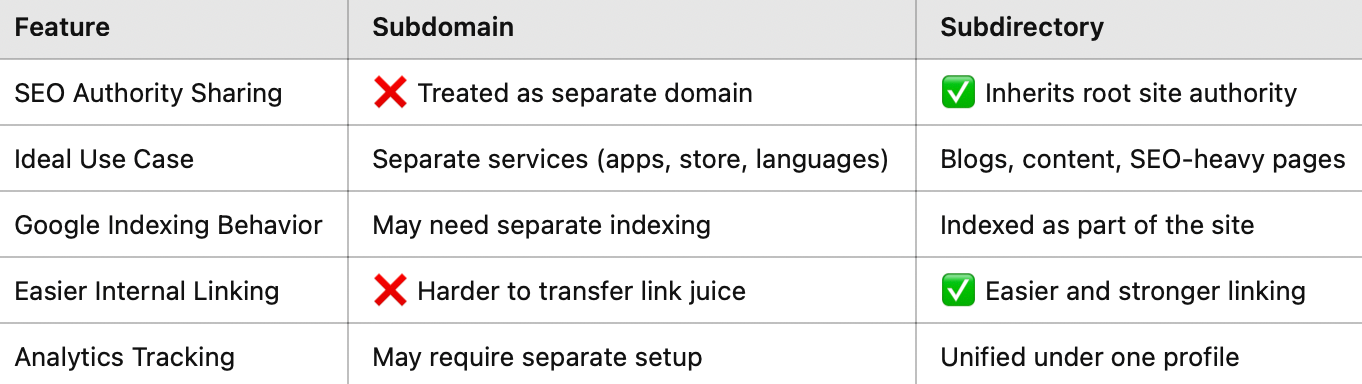
What Google Says:
Google’s John Mueller has said:
“Google can figure out that subdomains and subdirectories are connected, but it still treats them somewhat separately.”
So if ranking blog posts or content is your goal, subdirectories are better for SEO.
When to Use a Subdomain
Use a subdomain when:
- You’re building a web app or service (app.domain.com)
- You want to localize your site (ge.domain.com)
- You’re using a different tech stack or CMS for that section
👉 Create subdomains easily with Spaceship
When to Use a Subdirectory
Use a subdirectory when:
- You want content to boost your SEO (blogs, tutorials)
- You’re keeping everything under one website and CMS
- You want to maximize domain authority sharing
- You’re focusing on internal linking and branding
Subdirectories are like these:
- domain.com/blog
- domain.com/about
- domain.com/charts
How to Create Subdomains and Subdirectories with Spaceship
Subdomain Setup:
- Go to your Spaceship account dashboard
- Choose your domain > DNS Settings
- Add a new A or CNAME record
- Set your subdomain (e.g., blog) and point to your hosting
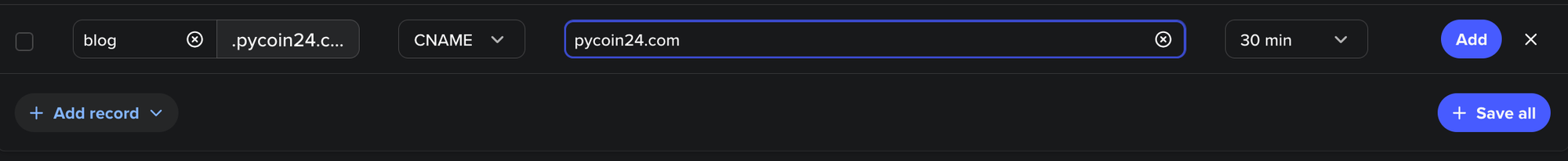
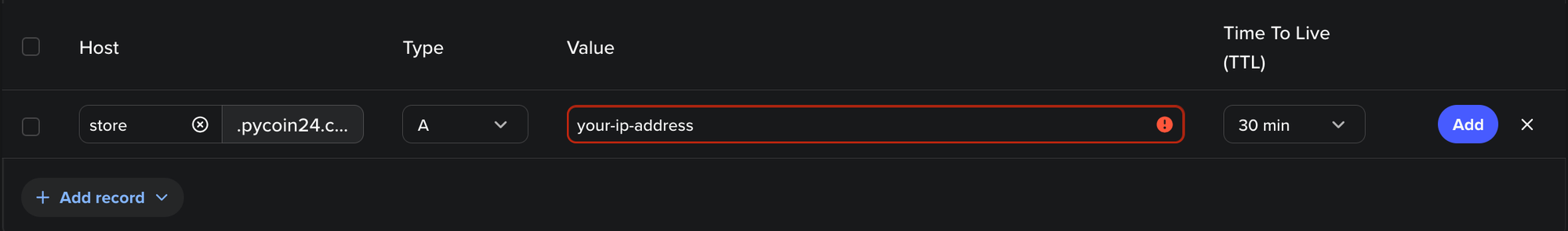
5. Save and you’re done (After few minutes should see green check)
Subdirectory Setup:
Subdirectories are configured on your web hosting platform or CMS, not your domain registrar. For example:
- WordPress: create a new page or install blog under /blog
- Hosting server: create a folder named blog or store inside your public HTML
You Don’t have to change DNS.
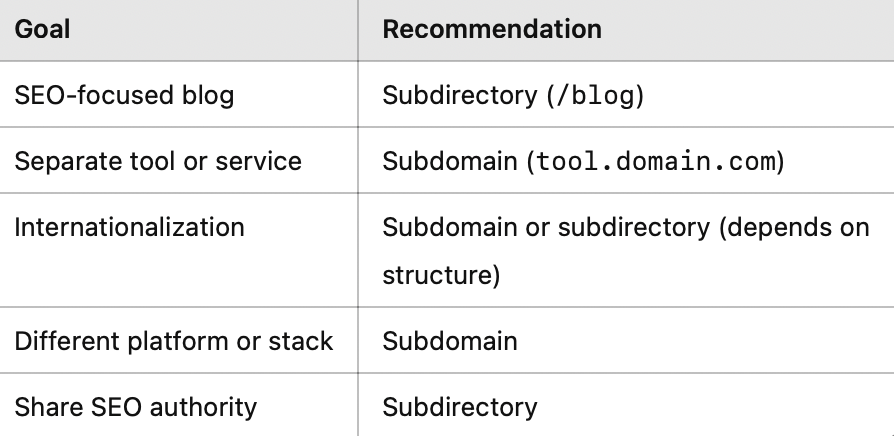
So, Which One Should You Use?
Related Articles
Final Thoughts
Both subdomains and subdirectories have their important place in website structure.
But if you’re serious about ranking content, growing organic traffic, and boosting SEO, then subdirectories give you a strong advantage.
If you’re building a separate service, testing tools, or working with different platforms, then subdomains can be better choice.
🎯 If Need an affordable domain provider with simple DNS tools?
You can fuel my next data science deep dive by buying me a coffee ☕!